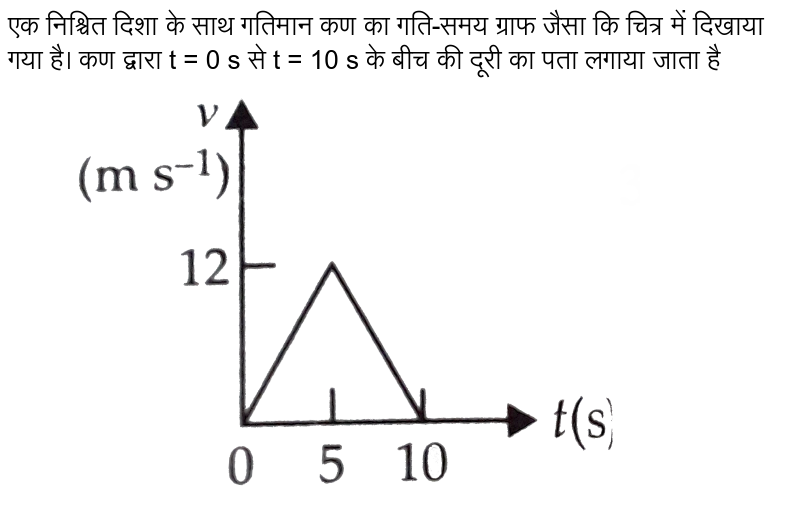
43 if we denote speed by s, distance by d and time by t, the relationship between these quantities is
If we denote speed by S , distance by D and time by T ... - Toppr Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ If we denote speed by S , distance by D and time by T the relationship these equation is? Solve Study Textbooks Guides. Join / Login >> Class 11 >> Physics >> Motion in a Straight Line >> Speed and Velocity >> If we denote speed by S , distance by D . Motion and Time Class 7 Extra Questions ... - Learn CBSE If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these Quantities is [NCERT Exemplar] Answer: (d) \(S=\frac{1}{T} \times D\) Question 6. Which one records the distance travelled by a vehicle? (a) Speedometer (b) Manometer (c) Motometer (d) Odometer Answer: (d) Odometer. Question 7.
If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the ... If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is. If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is. Sign Up. Sign Up to our social questions and Answers Engine to ask questions, answer people's questions, and connect with other people.

If we denote speed by s, distance by d and time by t, the relationship between these quantities is
plato.stanford.edu › entries › determinism-causalCausal Determinism - Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy Jan 23, 2003 · Physics, particularly 20 th century physics, does have one lesson to impart to the free will debate; a lesson about the relationship between time and determinism. Recall that we noticed that the fundamental theories we are familiar with, if they are deterministic at all, are time-symmetrically deterministic. CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 13 MCQ Objective of Motion ... If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is: [A]. S = D x T [B]. T = S/D [C]. S = 1 x D/ T [D]. S = T/D. View Answer; Q6 In a science quiz competition, Payel are asked a question where she had to choose the statement which was/were correct? ... NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Motion & Time Notes | Study ... Speed = Distance / Time. Distance = 54km = 54 x1000 = 54000m. Time = 90 minutes = 90×60= 5400s. Speed = 54000/5400 = 10 m/s. Q.5. If we denote speed by S, the distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is. (a) S = D × T. (b) T = S/D. (c) S = 1/SxD.
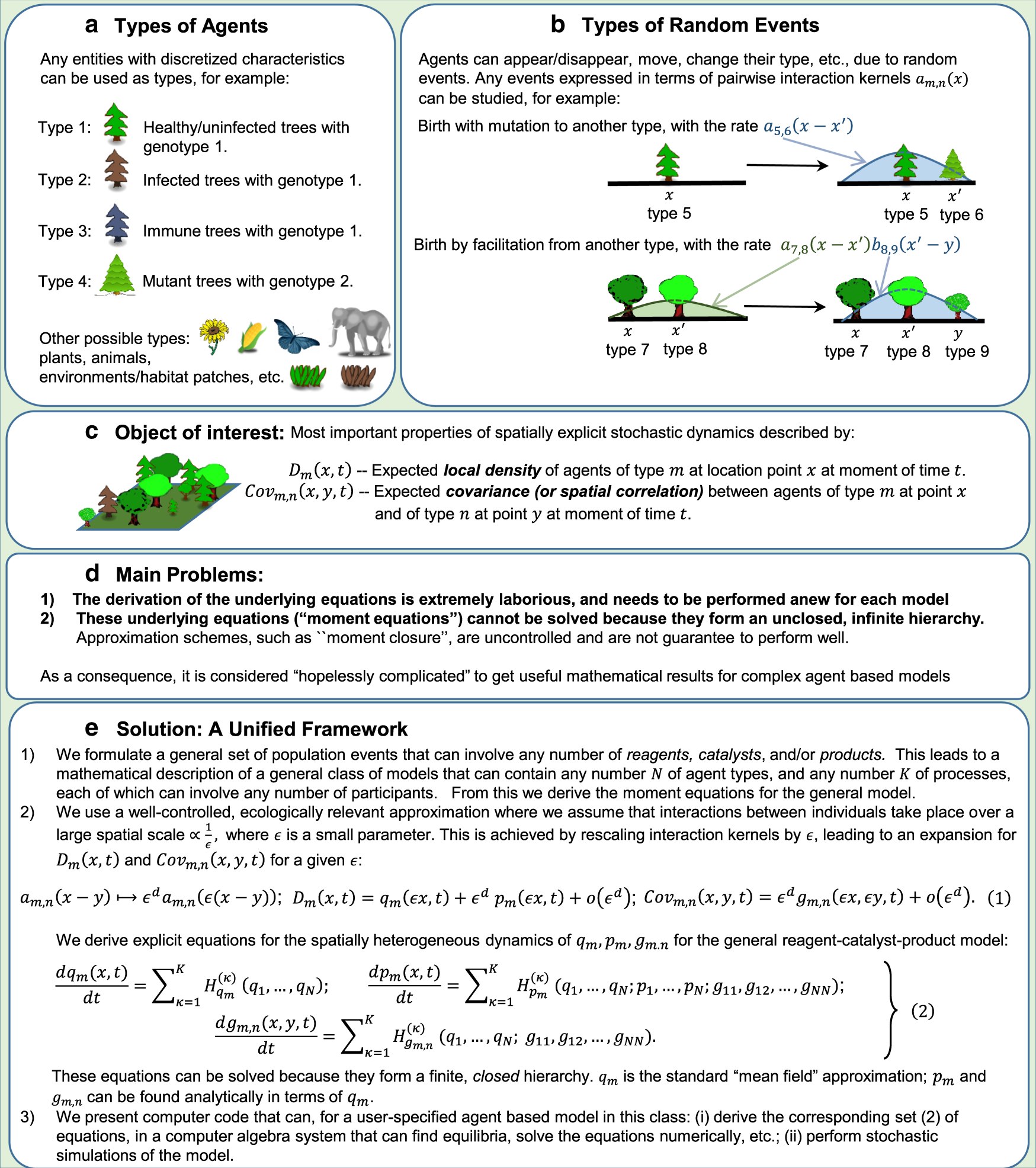
If we denote speed by s, distance by d and time by t, the relationship between these quantities is. 4.1 Related Rates - Calculus Volume 1 - OpenStax Since we are asked to find the rate of change in the distance between the man and the plane when the plane is directly above the radio tower, we need to find d s / d t d s / d t when x = 3000 ft. x = 3000 ft. Step 3. From the figure, we can use the Pythagorean theorem to write an equation relating x x and s: s: MCQ Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 13 Motion and ... If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is (a) S = D T (b) T = \(\frac{S}{D}\) (c) S = \(\frac{1}{T}\) × D (d) S = \(\frac{T}{D}\) ... We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 13 Motion and Time with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries ... NCERT Exemplar solutions for Class 7 Science ... - BYJUS Speed = Distance / Time. Distance = 54km = 54 x1000 = 54000m. Time = 90 minutes = 90×60= 5400s. Speed = 54000/5400 = 10 m/s. 5. If we denote speed by S, the distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is. NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Chapter 13 Motion and Time ... If we denote speed by 5, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is (a) S=D × T (b) T=S/D (c) S=1/T x D (d) S=T/D Solution: (c) Question 6. Observe figure. The time period of a simple pendulum is the time taken by it to travel from (a) A to B and back to A.
3.4 Motion with Constant Acceleration - University Physics ... We are asked to solve for time t. As before, we identify the known quantities to choose a convenient physical relationship (that is, an equation with one unknown, t.) Figure 3.24 Sketch of a car accelerating on a freeway ramp. Solution Again, we identify the knowns and what we want to solve for. We know that x 0 = 0, x 0 = 0, v 0 = 10 m/s, a = 2.00 m/ s 2 v 0 = 10 m/s, a = 2.00 … If we denote speed by S, the distance by D and time by T, the ... If we denote speed by S, the distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is (a) S = D × T (b) T = S/D (c) S = 1/TxD (c) S = T/D Answer: (c) S = 1/ T x D Speed is defined as the rate of change of position of an object in any direction. Physical Quantities and Units | Physics - Lumen Learning We define a physical quantity either by specifying how it is measured or by stating how it is calculated from other measurements. For example, we define distance and time by specifying methods for measuring them, whereas we define average speed by stating that it is calculated as distance traveled divided by time of travel.. Measurements of physical quantities are … › textbook › alternatingMeasurements of AC Magnitude | Basic AC Theory | Electronics ... We can measure the rate of alternation by measuring the time it takes for a wave to evolve before it repeats itself (the “period”), and express this as cycles per unit time, or “frequency.” In music, frequency is the same as pitch , which is the essential property distinguishing one note from another.
3.4 Motion with Constant Acceleration – University Physics ... We then simplify the equation. The units of meters cancel because they are in each term. We can get the units of seconds to cancel by taking t = t s, where t is the magnitude of time and s is the unit. Doing so leaves . We then use the quadratic formula to solve for t, which yields two solutions: t = 10.0 and t = −20.0. A negative value for ... If we denote speed by S, the distance by D and time by T ... Find an answer to your question If we denote speed by S, the distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is dilipkamaliyar171 dilipkamaliyar171 29.08.2020 Science Primary School answered If we denote speed by S, the distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is 2 See answers ... if we denote speed by s, distance by d and time t what is the ... If we denote speed by s, distance by d and time t what is the relationship between these quantities 2 See answers Advertisement Answer 4.6 /5 53 maya30 s=d/t speed = distance upon time Advertisement Answer 4.7 /5 34 sanskarcr7 speed= distance / time . Advertisement Still have questions? Find more answers Ask your question New questions in Physics en.wikipedia.org › wiki › SpacetimeSpacetime - Wikipedia The difference of the two readings of W 1 and W 2 is the temporal distance of the two events in S, and their spatial distance is d. The difference of the two readings of W′ is the temporal distance of the two events in S′. In S′ these events are only separated in time, they happen at the same place in S′.
If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the ... The relationship between speed (s), distance (d) and time (t) is given by s=dt find the value of s, if d=135 meters and t= 10 seconds. play.2 answers · Top answer: `S=DxxT` `T=(S)/(D)` T=D/S S=D-T Answer: C
Question 5 If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time ... If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is (a) S=DT (b) T = S D (c) S= 1 T ×D (d) S= T D Solution Distance = speed × time. So, the answer is (c). Suggest Corrections 0 Similar questions Q. Directions: In these questions, relationship between different elements is shown in the statements.
MCQ Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 13 Motion and ... 03.10.2020 · If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is (a) S = D T (b) T = \(\frac{S}{D}\) (c) S = \(\frac{1}{T}\) × D (d) S = \(\frac{T}{D}\) Answer . Answer: (c) S = \(\frac{1}{T}\) × D. Question 3. Observe the figure given below: The time period of a simple pendulum is the time taken by it to travel from (a) A to B …
Distance measures (cosmology) - Wikipedia Distance measures are used in physical cosmology to give a natural notion of the distance between two objects or events in the universe.They are often used to tie some observable quantity (such as the luminosity of a distant quasar, the redshift of a distant galaxy, or the angular size of the acoustic peaks in the cosmic microwave background (CMB) power spectrum) to …
pressbooks.online.ucf.edu › osuniversityphysics3.4 Motion with Constant Acceleration – University Physics ... At t = 10 s, a particle is moving from left to right with a speed of 5.0 m/s. At t = 20 s, the particle is moving right to left with a speed of 8.0 m/s. Assuming the particle’s acceleration is constant, determine (a) its acceleration, (b) its initial velocity, and (c) the instant when its velocity is zero.
MCQ Motion and Time Chapter 13 Class 7 Science - eVidyarthi MCQ Motion and Time Chapter 13 Class 7 Science. 1. A bus travels 54 km in 90 minutes. The speed of the bus is. 2. If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is. 3. Observe the figure given below: 4.
NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Chapter 13 Motion and Time ... (b) 10 m/s (c) 5.4 m/s (d) 3.6 m/s Answer: (b) As, we know that. Question 5: If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is Answer: (c) The correct relationship is. Question 6: Observe the given figure. The time period of a simple pendulum is the time taken by it to travel from (a) A to B and ...
Speed, Distance and Time Formula: Definition and Solved ... Speed is directly related to distance and time. This is because, speed of an object refers to the distance travelled divided by time and it expressed as : Speed = distance/time s = d/t Furthermore, one can also explain the relationship of time with other two variables using this formula. Time = distance/speed t = d/s And, distance = speed × time
Class 7 Important Questions for Science - Motion and Time If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is (a) S = D × T (b) T = S / D (c) S = 1 / T * D (d) S = T / D; Observe Figure 13.3. The time period of a simple pendulum is the time taken by it to travel from (a) A to B and back to A.
If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the ... If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is * * (a) S = D/ T (b) T = SD (c) S = 1T × D (d) S = TD 2 See answers Advertisement Advertisement RamArora RamArora Answer: a)S=D/T is the correct answer for sure . Explanation:
If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the ... If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is :a. S=D… Get the answers you need, now! sworldwidehr sworldwidehr 18.05.2020 Science Secondary School answered If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is : a. S=D ×T
If We Denote Speed By S, Distance By D And Time By T, The ... Class 7 Science / MCQs on Motion and Time Choose an option to see the answer | Answer another question | Take a practice test If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is\r\n
NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Chapter 13 Motion and Time If we denote speed by 5, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is (a) S=D × T (b) T=S/D (c) S=1/T x D (d) S=T/D Solution: (c) Question 6. Observe figure. The time period of a simple pendulum is the time taken by it to travel from (a) A to B and back to A.
ACP - Box model trajectory studies of contrail formation ... 18.01.2022 · The simulated time t sim is 2 s. In the following, we describe the initial conditions (Sect. 2.4.1) and introduce important diagnostics, including explanations about the averaging procedure for ensemble mean runs (Sect. 2.4.2). Table 1Baseline parameters of all regular LCM simulations (first three rows) and those corresponding to the box model set-up of Lewellen (last …
if-we-denote-speed-by-s-the-di - Lido Learning Question 5. If we denote speed by S, the distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is.1 answer · Top answer: The answer is (c) S = 1/SxD Explanation: Option c) is the correction equation because Speed = Distance/Time
Ohm’s Law Practice Worksheet With Answers Worksheet ... The key to understanding this concept is to realize that the transistor’s switching time must be much faster than the time it takes for the light bulb’s filament to fully heat or fully cool. The situation is analogous to throttling the speed of an automobile by rapidly “pumping” the accelerator pedal. If done slowly, the result is a varying car speed. If done rapidly enough, …
Time, Velocity, and Speed | Physics - Lumen Learning To find elapsed time, we note the time at the beginning and end of the motion and subtract the two. For example, a lecture may start at 11:00 A.M. and end at 11:50 A.M., so that the elapsed time would be 50 min. Elapsed time Δ t is the difference between the ending time and beginning time,
Oswaal CBSE Question Bank+Pullout Worksheets Class 7 (Set of ... Oswaal Editorial Board · 2021 · Study AidsIf we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is : (NCERT Exemplar) (a) S = DT (b) T = S D (a) ...
Redshift - Wikipedia The Hubble law's linear relationship between distance and redshift assumes that the rate of expansion of the universe is constant. However, when the universe was much younger, the expansion rate, and thus the Hubble "constant", was larger than it is today. For more distant galaxies, then, whose light has been travelling to us for much longer times, the approximation …
Oswaal NCERT & CBSE Question Bank Class 7 (Set of 6 Books) ... Oswaal Editorial Board · 2021 · Study AidsIf we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is : (NCERT Exemplar) (a) S = DT (b) T = S D (a) ...
Dynamics and Vibrations: Conservation Laws for Particles ... If the vehicle travels a distance d between stops, the time between two stops is 2d/V. The average power is therefore . Taking V ... Let V denote the wind speed, and let denote the density of the air. 1. In a time t, a cylindrical region of air with radius R and height Vt passes through the fan. 2. The cylindrical region has mass 3. The kinetic energy of the cylindrical region of air is 4. …
10. If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T ... If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is taniya4486 taniya4486 29.05.2020 Physics Secondary School answered 10. If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is 2 See answers
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › EarthEarth - Wikipedia The orbital speed of Earth averages about 29.78 km/s (107,200 km/h; 66,600 mph), which is fast enough to travel a distance equal to Earth's diameter, about 12,742 km (7,918 mi), in seven minutes, and the distance to the Moon, 384,000 km (239,000 mi), in about 3.5 hours.
Distance Speed Time Formula - Softschools.com The speed is: s = 27.0 km/h. s = 7.50 m/s. Converting the units, the speed is 7.50 m/s. The time the cart traveled for was: t = 10.0 min. t = 600s. The speed of the cart and the time of travel are given, so the distance traveled can be found using the formula: d = st. d = (7.50 m/s)(600 s) d = 4500 m. The golf cart traveled 4500 m, which is ...
Distance/Speed Relation: Velocity Formula and Practice ... The speed is the time rate of change of the distance. If 'D' is the distance of an object in some time 'T', the speed is equal to, s = D/T. It has the same units as velocity. let us solve some examples, we will introduce the formulae as we go along. Examples. Example 1: The speed of a bus is 54 km/h if we don't let it stop at any point.
How Are Speed, Distance and Time Related? - Reference.com The relationship for speed is the same for any units, as long as the units are consistent. If a car traveled 30 miles in an hour, the speed would be 30 miles per hour. If an object is moving at varying speeds, then the relationship between speed, distance and time can only be used to calculate the average speed.
› journal › paperinformationStar Mass Inertia Dictates the Speed of Light The orbital speed (long-dashed line, km/s) and distance (D = 3ln(10R)) of each planet (hollow circle) relative to the Sun (D = 0). The letter R = 1 (1 astronomical unit, 15,000,000 km) is the distance between the Sun and the Earth. Short-dashed lines separate different shear bands of nebula circular rings.
If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the ... If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is motion and time class-7 Share It On FacebookTwitterEmail Please log inor registerto add a comment. 1Answer 0votes answeredJan 23, 2018by sameer(54.6kpoints) selectedJan 27, 2018by sarthaks Best answer Answer is ----
PDF Motion and Time - NCERT (a) 0.6 m/s (b) 10 m/s (c) 5.4 m/s (d) 3.6 m/s 5. If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is (a) S = D × T (b) T = S D (c) S = 1 D T × (d) S = T D 6. Observe Figure 13.3. Fig 13.3 The time period of a simple pendulum is the time taken by it to travel from (a) A to B and back to A. (b) O ...
NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Motion & Time Notes | Study ... Speed = Distance / Time. Distance = 54km = 54 x1000 = 54000m. Time = 90 minutes = 90×60= 5400s. Speed = 54000/5400 = 10 m/s. Q.5. If we denote speed by S, the distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is. (a) S = D × T. (b) T = S/D. (c) S = 1/SxD.
CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 13 MCQ Objective of Motion ... If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is: [A]. S = D x T [B]. T = S/D [C]. S = 1 x D/ T [D]. S = T/D. View Answer; Q6 In a science quiz competition, Payel are asked a question where she had to choose the statement which was/were correct? ...
plato.stanford.edu › entries › determinism-causalCausal Determinism - Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy Jan 23, 2003 · Physics, particularly 20 th century physics, does have one lesson to impart to the free will debate; a lesson about the relationship between time and determinism. Recall that we noticed that the fundamental theories we are familiar with, if they are deterministic at all, are time-symmetrically deterministic.

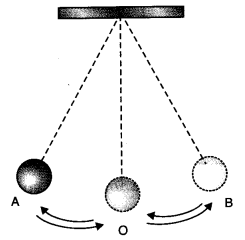

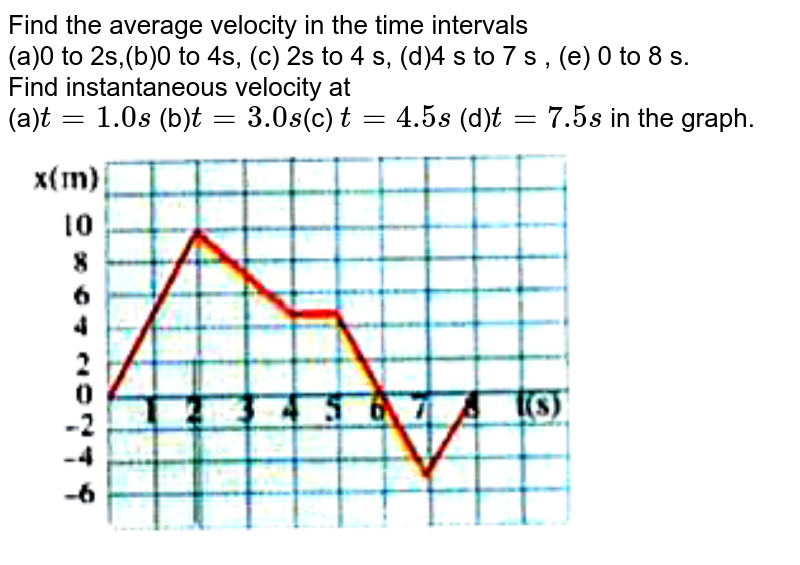











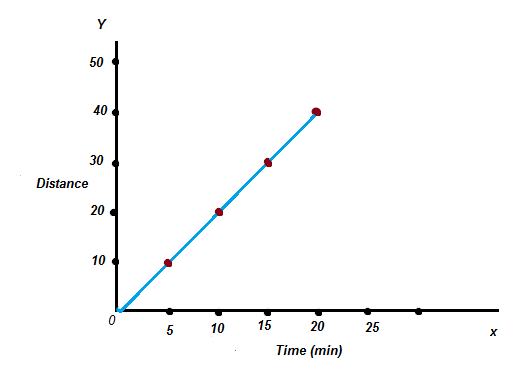











0 Response to "43 if we denote speed by s, distance by d and time by t, the relationship between these quantities is"
Post a Comment